Common Pitfalls in Building Regulations Compliance and How to Avoid Them
Building regulations are a crucial aspect of any construction project, ensuring that structures are safe, energy-efficient, and adhere to established standards. However, achieving compliance can be a complex and challenging process. In this blog, we will explore some of the common pitfalls that builders and developers often encounter in their journey towards building regulations compliance and provide valuable tips to steer clear of these obstacles.
Lack of Early Engagement with Authorities
One of the primary mistakes builders make is not engaging with local building authorities early in the planning process. Failure to consult with regulatory bodies from the outset can lead to misunderstandings, delays, and costly revisions later on. To avoid this pitfall, initiate communication with relevant authorities during the project’s conceptualization phase. Seek their guidance to ensure your plans align with local building codes and regulations.
Inadequate Documentation
Insufficient or inaccurate documentation is a prevalent stumbling block in compliance efforts. Detailed and precise documentation is crucial for demonstrating compliance with building regulations. To avoid this pitfall, create a comprehensive set of plans and specifications that clearly outline how your project meets all applicable requirements. Regularly update these documents as the project progresses and changes are made.
Ignoring Accessibility Standards
Accessibility is a key consideration in building regulations, and overlooking it is a common mistake. Failing to adhere to accessibility standards can result in legal consequences and delayed project timelines. To avoid this pitfall, incorporate accessible design features from the beginning, such as ramps, elevators, and wider doorways. Stay informed about current accessibility standards to ensure your project is compliant.
Energy Efficiency Oversights
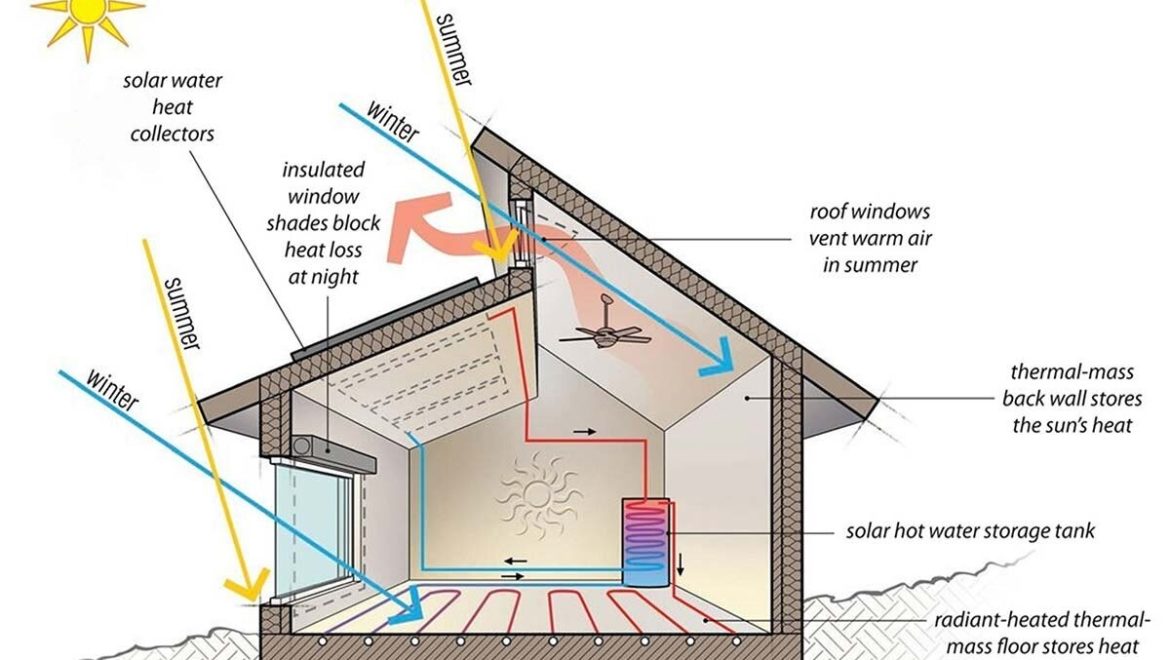
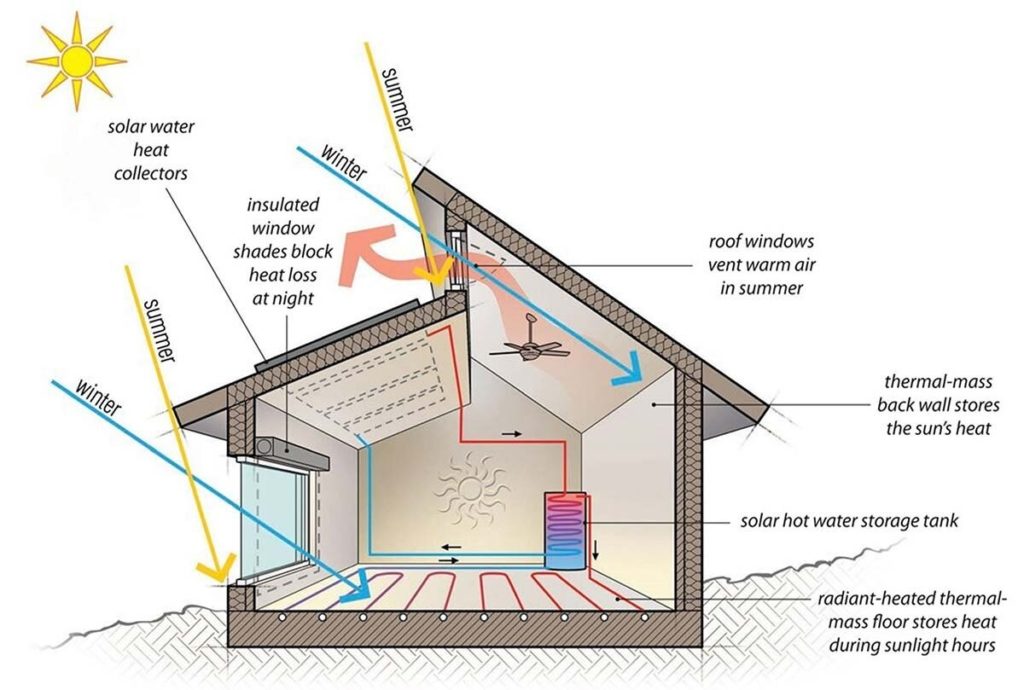
With a growing emphasis on sustainability, energy efficiency regulations are becoming more stringent. Ignoring these requirements can lead to increased operational costs and environmental impact. To avoid this pitfall, incorporate energy-efficient design elements and materials into your project. Stay updated on the latest advancements in green building technologies and consider obtaining certifications such as LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) to demonstrate your commitment to sustainability.
Poor Communication Among Stakeholders
Communication breakdowns among project stakeholders can hinder compliance efforts. Architects, engineers, contractors, and regulatory authorities must be in sync throughout the construction process. Establish a clear communication protocol, conduct regular project meetings, and foster collaboration among team members to ensure everyone is aligned with the project’s compliance goals.
Neglecting Regular Inspections
Some builders mistakenly assume that inspections are only necessary at the project’s completion. Regular inspections throughout the construction process are crucial to identify and rectify compliance issues promptly. Schedule inspections at key milestones, and address any non-compliance issues immediately to prevent them from snowballing into major problems.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of building regulations compliance requires diligence, communication, and a proactive approach. By avoiding common pitfalls such as late engagement with authorities, inadequate documentation, accessibility oversights, energy efficiency neglect, poor communication, and infrequent inspections, builders and developers can ensure their projects meet the necessary standards. Embracing a culture of compliance from the project’s inception will not only save time and resources but also contribute to the creation of safer, more sustainable structures.