All there is to know about a cavity wall
What is a cavity wall?
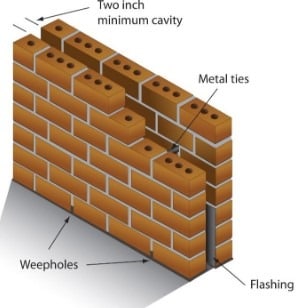
A cavity wall is constructed with two separate walls for single wall purposes with some space or cavity between them. They can be described as consisting of two “skins” separated by a hollow space (cavity). The skins typically are masonry, such as brick or cinder block. Masonry is an absorbent material that can slowly draw rainwater or even humidity into the wall. One function of the cavity is to drain water through weep holes at the base of the wall system or above windows.
What is the purpose?
The purpose of a cavity wall is to ensure that the inner skin of the wall remains dry and that no moisture penetrates the inside of the building.
History of the cavity wall –
Cavity walls existed in Greek and Roman times, but only developed as a component of more recent construction in the 18th and 19th centuries. Even during this time, they were very rare. The use of metal ties to connect the two skins only emerged in the second half of the 19th century and then became more common towards the beginning of the 20th century. In the UK, most new, external masonry walls have been cavity walls since the 1920s.
Insulation –
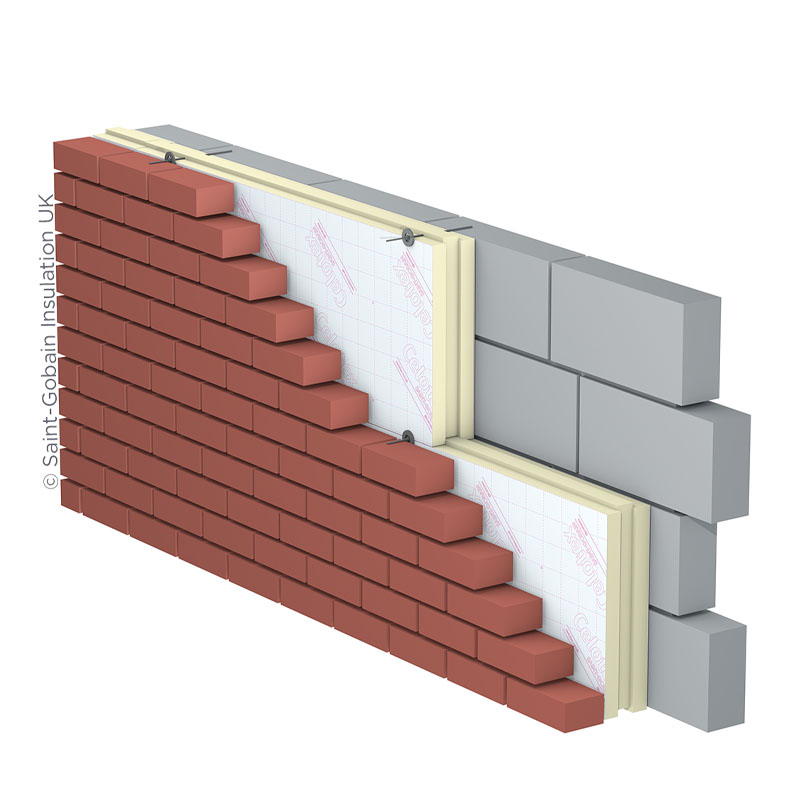
Cavity wall insulation is used to reduce heat loss. This happens by filling the air space with material that inhibits heat transfer. This immobilises the air within the cavity, preventing convection, and can substantially reduce space heating costs.
During the construction of new buildings, cavities are often filled with glass fibre wool or mineral wool panels placed between the two sides of the wall.
Advantages of cavity walls –
- They act as good sound insulators
- Economically they are cheaper than solid walls
- They also reduce the weights on foundation because of their lesser thickness
- Moisture content in outer atmosphere is not allowed to enter because of hollow space between the skin. So, they prevent dampness
- Cavity walls give better thermal insulation than solid walls. It is because of the space provided between two skins of cavity walls is full of air and reduces heat transmission into the building from outside.