A guide to Passive houses: definition, benefits and cost
Passive house design is an alternative to regular heating. Instead of having a boiler and radiators, they use a special ventilation system and effective insulation. Read on to find out more about passive house standards
What is a passive house?
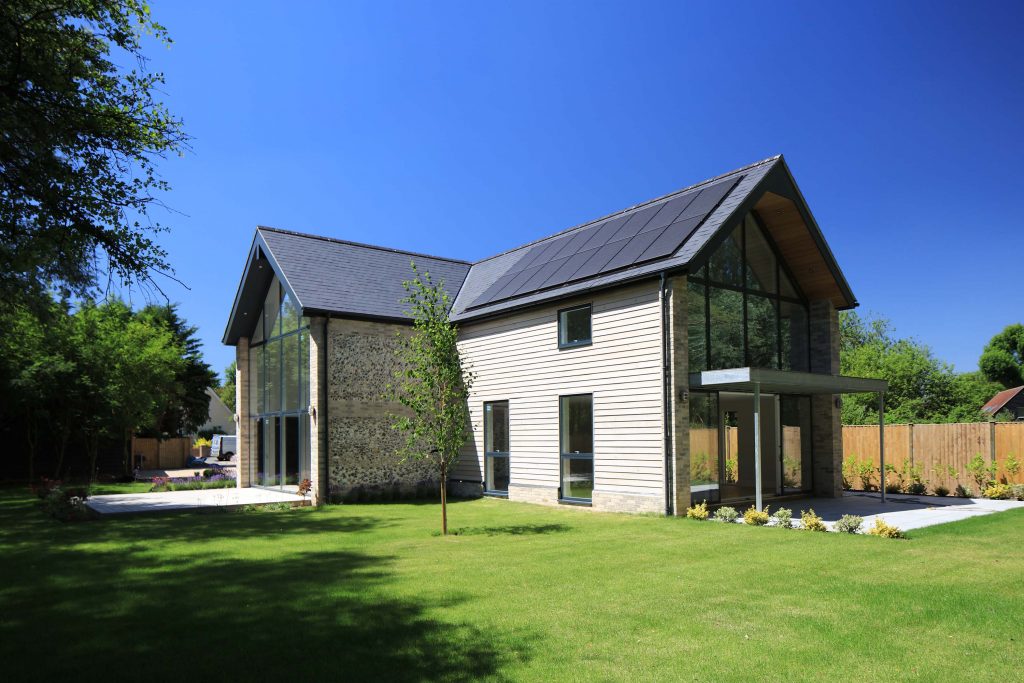
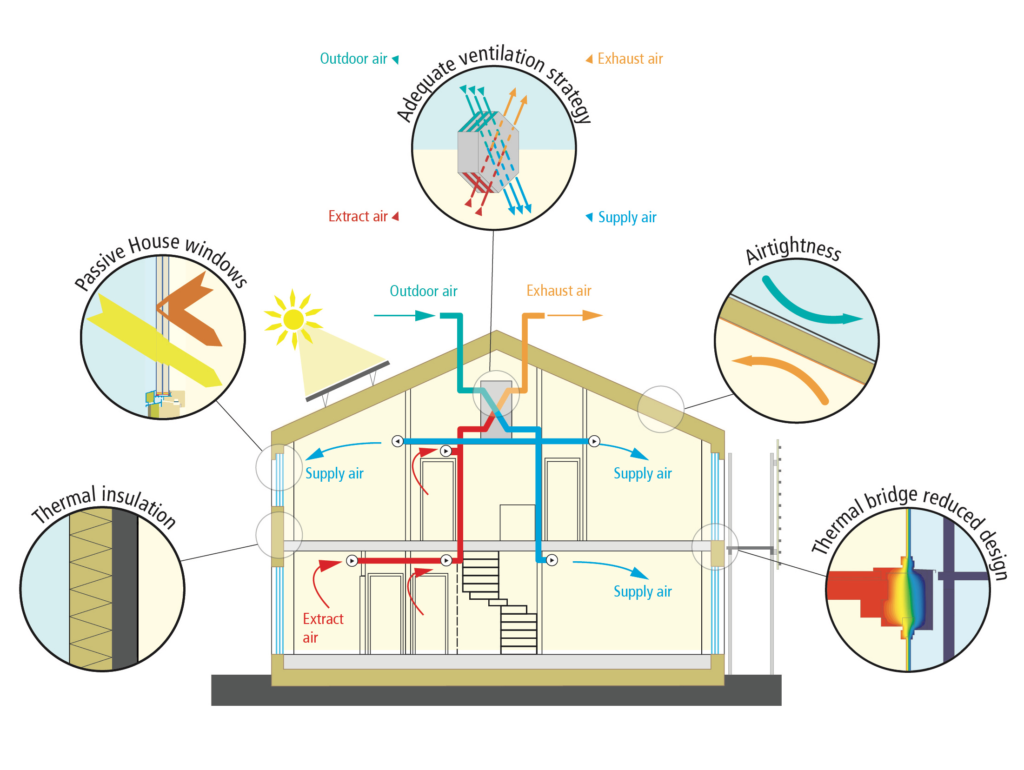
A passive house is a design standard that is energy efficient, comfortable, affordable and ecological all at the same time. The houses attain thermal comfort with minimal heating and cooling. They achieve this by using insulation, appropriate windows and doors, airtightness, elimination of thermal bridges and ventilation systems with heat recovery.
Who invented the passive house?
The idea of the house was created by researchers in Germany however, they were originally called passivhaus. It all started with early conversations in the 1980s, led by academics Bo Adamson and Wolfgang Feist. Later, their concept was further developed through a number of research projects.
What are the requirements for passive houses?
To achieve the passive house standard, you must meet several criteria, such as:
- Airtightness – these houses are very airtight and shouldn’t have no more than 0.6 air changes per hour at 50 pascals pf pressure.
- Space heating – The energy demand for space heating must not exceed 15 kWh/m2 of living space per year or 10W/m2 at peak demand. This contrasts with the 100W/m2 needed in a typical house.
- Thermal comfort – Living areas should be comfortable all year round, with no more than 10% of the hours in a given year exceeding 25°C.
- Primary energy – Total energy needed for all domestic applications (heating, hot water and domestic electricity) must not exceed 60 kWh/m2of living space per year.
Are passive houses expensive?
Passive buildings don’t require the expensive heating or cooling systems of conventional buildings. This means even though the buildings require high quality materials they are still affordable. Also, they make for a great investment because you save long term on energy bills.
Advantages –
- Affordability
- Lower heating costs
- Energy saving
- More durable buildings
Disadvantages –
- Boxy and ugly – although there are many benefits of passive houses, many people think the homes look boxy and ugly. This is because it relates to the total surface area of all of the external walls (the Heat Loss Area) divided by the total floor area. A lower number means there’s less surface area for heat to escape.
- They don’t add value when resold – one of the main reasons that people don’t buy passive houses in the UK is because they don’t add much value. The owners usually live in them for the rest of their lives.
- These homes don’t fit in every location – it must be constructed in a location that allows uninterrupted sunshine to reach the south side of the home. In some big cities, this might be a problem.
- Noise concerns – because they are airtight noise can’t enter or leave a passive house. tiny noises will be audible throughout the entire building.