Green Belt Areas: Everything You Need To Know
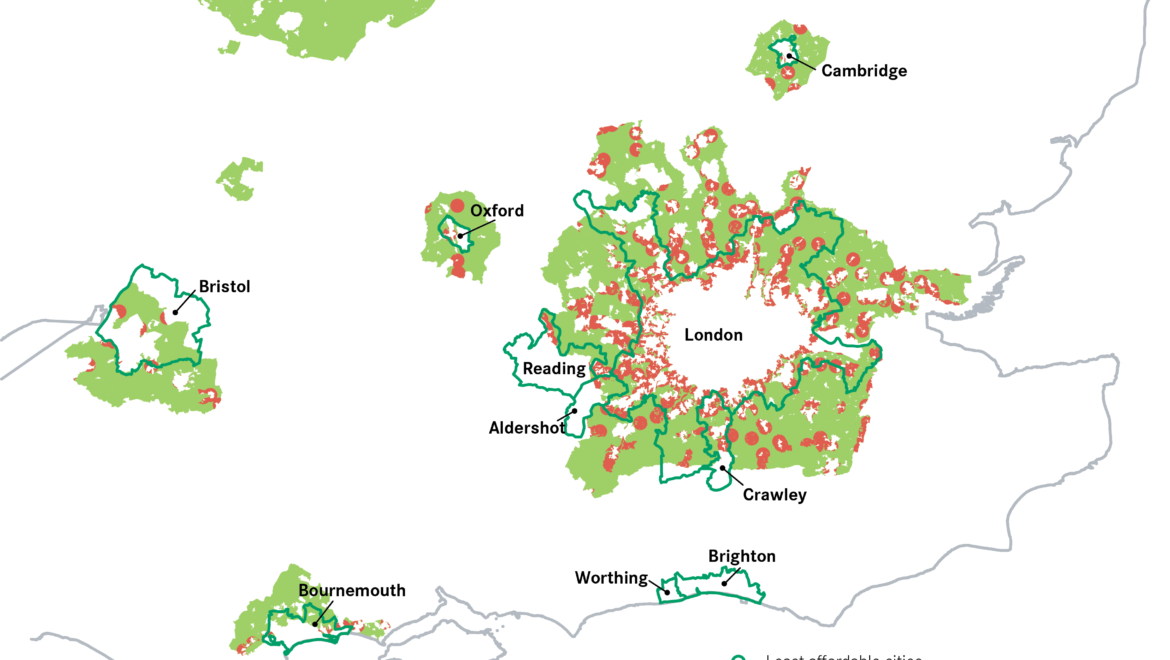
England’s 14 green belts cover around 12.4% of land in the country and provide a breath of fresh air for 30 million people.
What is a green belt area?
A green belt is a policy and land use zone designation used in land use planning. They retain areas of largely undeveloped, wild, or agricultural land surrounding or neighboring urban areas.
There are three different types of land and they are:
- Brownfield – land that has been built on previously, but is now vacant or in need of redevelopment.
- Greenfield – land that has not been built on before (agricultural/grassland).
- Green belt – highly protected land with tight restrictions on development.
Local planning authorities are extremely cautious about their green belt areas. This is because the purpose of one is to capture the fugitive emissions emanating from plant operations, alternate the noise generated and improve the aesthetic.
New homes can be allowed in the green belt if they meet the need. And this exception only applies to specific policies in the local plan. And only then if the need for those homes is clearly demonstrated they will be able to live in a green belt area. Developers need to submit a case for very special circumstances in which the building would outweigh the resulting harm to the environment.
How much does it cost to buy green belt land?
The cost of the land largely depends on whether it has planning permission or not. Green belt land is usually cheap if it doesn’t have consent to build on. It is cheap because of the strong building restrictions. However, if the area has consent to build on it could sell for about £500,000 per acre.
Green belts are intended to check further growth of large built-up areas such as London. This is because they need to prevent neighboring towns from merging into one another.
You definitely can’t overlook the benefits that green belts can offer for your health and wellbeing. For example, being in the countryside where it’s rich with nature, and there’s plenty of fresh air for everyone to enjoy. They also double up as local nature reserves. So, they work brilliantly for wildlife, allowing creatures to move between habitats safely and flourish in a mix of landscapes.
Instead of viewing the Green Belts as a limitation to building more homes, we need to focus on restoring and enhancing the land. So, it can continue to provide a space for nature and a place to relax, play and grow our food.